Hi everyone ! This week’s Post 2 delves into theoretical approaches to learning environment design and their practical application. I’ll be zeroing in on ‘Experiential Learning’.
What is Experiential Learning?
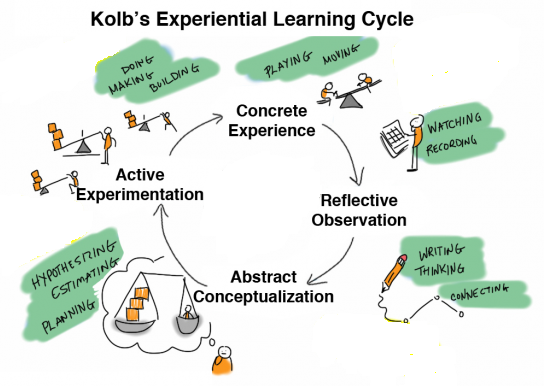
Experiential learning, as its name implies, is an educational approach where knowledge, skills, and values are gained through direct ‘experience’. It goes beyond passive information absorption, emphasizing learning by actively doing. Based on my research, experiential learning is characterized as a ‘philosophy and methodology’ where educators immerse learners in hands-on experiences and meaningful reflection.
A key feature of this learning method is its ability to cultivate critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It also enhances learners’ capacity to apply knowledge in real-world contexts. The approach isn’t solely focused on outcomes but also values the learning ‘process’ itself. Effective experiential learning requires a thoughtful balance of reflection, content, and active engagement.
Incorporating Experiential Learning into My Design
I have a deep passion for economics and innovative educational approaches, particularly in creating engaging learning resources like educational comics. I firmly believe that applying experiential learning principles within economics can help students develop a more profound and practical understanding of complex economic concepts.

In an ‘Economics’ course, I would move beyond traditional theoretical lectures by designing interactive and immersive learning experiences. For instance, students could simulate market dynamics by creating a hypothetical startup and navigating its financial challenges, or they might critically analyze real-world economic policies to predict potential societal impacts. Through these hands-on, immersive activities, learners can naturally internalize fundamental economic principles like supply and demand or cost-benefit analysis by directly experiencing their practical applications within a controlled, supportive environment.
When developing educational comics or animation scripts to explain economic theories, experiential learning becomes an incredibly powerful pedagogical tool. Picture students crafting narratives that illustrate complex concepts like inflation through relatable daily life scenarios or exploring comparative advantage through engaging trade narratives. The process of researching economic principles, structuring compelling storylines, and creating visual representations; while confronting and overcoming design challenges – transforms into a rich, transformative learning experience. Through this approach, students don’t merely memorize theoretical concepts; they actively construct and internalize economic knowledge by creatively applying their understanding.
By emphasizing active engagement, experiential learning provides students with a robust framework for independent discovery and meaningful intellectual growth, effectively bridging the often-perceived gap between abstract economic theory and real-world practical application.
References
- The Association for Experiential Education. (2024). What is experiential learning? Experiential Learning. https://www.experientiallearning.org/info/what-is-experiential-learning/?v=3e8d115eb4b3
- Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. (n.d.). Experiential learning. Northern Illinois University. https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/experiential-learning.shtml
- Study.com. (n.d.). Experiential learning: Definition, methods & examples. https://study.com/learn/lesson/experiential-learning-techniques-examples.html
Hi Tony !
I appreciated how you connected direct instruction to personal experiences in math and science—this approach made the explanation both engaging and accessible. I concur with your observation that the method’s primary advantage lies in the instructor’s immediate intervention when students encounter confusion, which is particularly crucial in progressively complex subjects.
Your assessment of the pet health project was also insightful. I found your comparison between direct instruction’s structured framework and inquiry-based learning’s adaptability compelling, especially considering the individualized nature of pet care. Your suggestion of a blended approach is intriguing—using direct instruction to establish foundational health knowledge, then transitioning to inquiry-based learning for applying those principles to diverse pet scenarios seems like an effective strategy.
Recent Comments